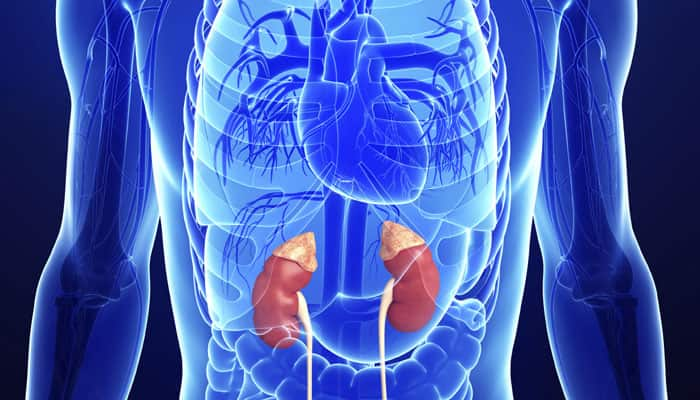
New Delhi: Your body needs phosphorous in order to build and repair strong healthy bones. Phosphorous is also important to help nerves function and keep other parts of your body healthy. It is the second most abundant mineral in the body - next to calcium.
The kidneys help remove extra phosphorus in your blood. However, when you have chronic kidney disease (CKD), your kidneys cannot remove phosphorus very well. This can result in high phosphorus levels, causing damage to your body.
As per doctors, excess phosphorous in human body can cause chronic kindey diseases, including hyperphosphatemia - in which phosphate levels shoot up abnormally high.
Symptoms of hyperphosphatemia include muscle cramps, numbness, tingling, bone or joint pain, and rash.
"Occasionally patients with hyperphosphatemia report hypocalcemic symptoms such as muscle cramps, numbness or tingling. Other symptoms may include bone or joint pain, and rash. More commonly, patients witness fatigue, shortness of breath, anorexia, nausea, vomiting, disturbed sleep," said Sudeep Singh Sachdev, Consultant Nephrology at Max Super Speciality Hospital, on Wednesday.
People should consult doctors at the earliest if they experience the symptoms of hyperphosphatemia.
Sachdev said that specific blood test are performed to diagnose hyperphosphatemia which measures phosphate, calcium, magnesium, blood urea nitrogen and parathyroid hormone (PTH) for diagnosis.
It is important to diagnose and find the underlying cause of hyperphosphatemia to treat and restore normal phospate metabolism.
“The medication used for hyperphosphatemia includes phosphate binders which block the absorption of phosphates from the gut. This includes aluminum hydroxide, calcium carbonate, calcium acetate, magnesium hydroxide, sevelamer hydrochloride, Sachdev said.
"Loop diuretics help to increase phosphate excretion through the kidneys. These drugs include Furosemide, Bumetanide," said Sachdev, adding that various medication can help normalise the phosphate levels in the blood.
According to medical sciences dietary modification or consuming low phosphorus diet is also necessary especially in case of kidney patients.
Neerja Jain, Nephrology department of Ram Manohar Lohia (RML) hospital said: "Dietary change alone may be sufficient to restore blood phosphate levels provided the kidneys function efficiently.”
Foods that should be strictly avoided, or at least consumed in moderation includes manufactured drinks and foods such as soft drinks, chocolates, tinned milk, processed meat, among others.
"Besides dietary restriction, removal of phosphates through dialysis or intensive (nocturnal or short daily) dialysis regimens can also be implemented, this modality of treatment often proves beneficial," said Jain.
Like phosphate, high calcium levels also lead to dangerous calcium deposits in blood vessels, lungs, eyes, and heart. Therefore, both phosphorus and calcium control are very important for your overall health.
(With IANS inputs)